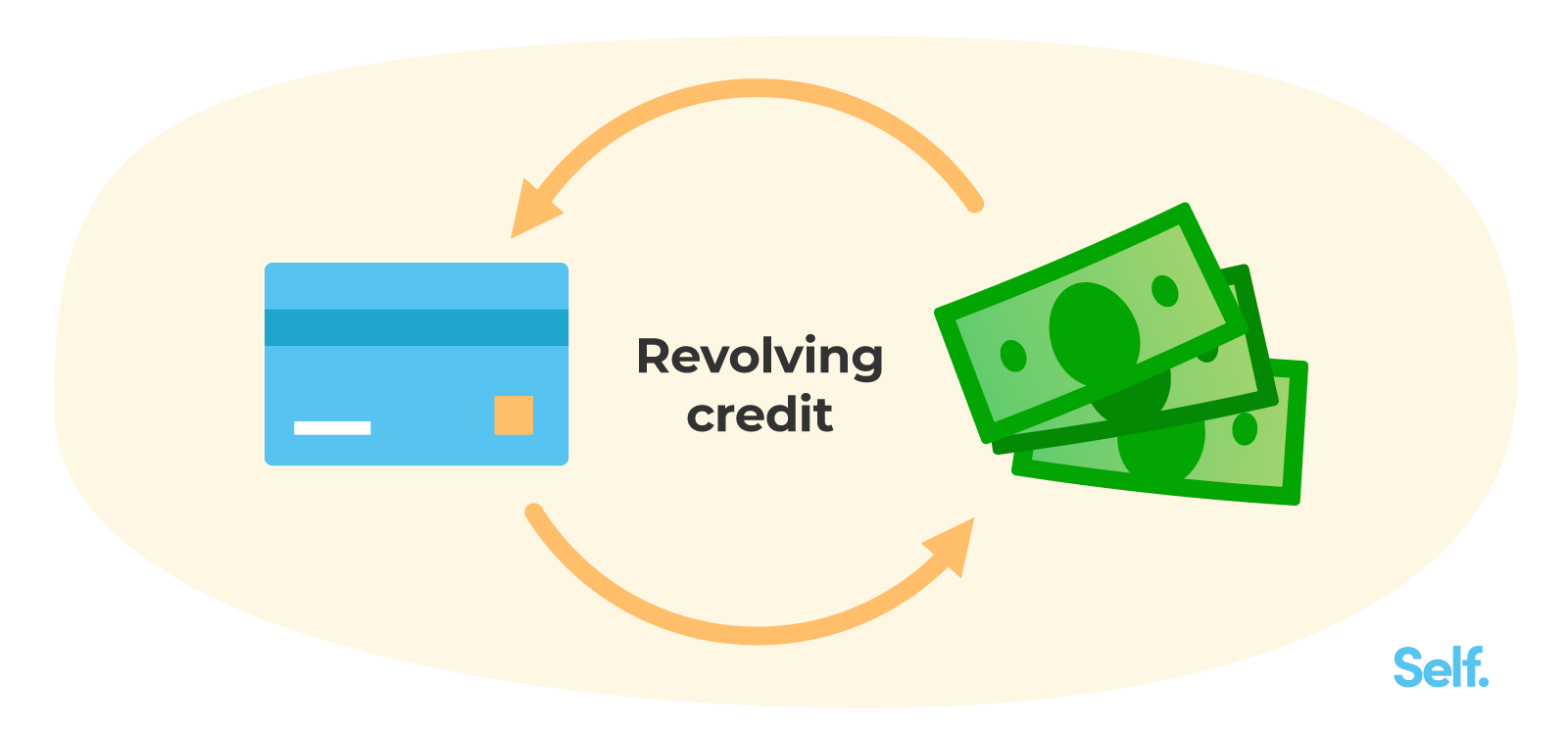
What Is Revolving Credit?
A revolving loan is a line of credit that can still be used even if the balance is paid in full. Borrowers can borrow up to a certain amount, after which they can access that loan amount regularly. You can repay the balance in full or make regular payments. Each payment will reopen the account holder’s credit, minus any accrued interest and fees. Examples of revolving credit include credit cards, lines of credit, and home equity lines of credit (HELOCs). It works differently than installment payments. Learn more about the pros and cons of loan refinancing.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A revolving line of credit is a line of credit that remains in effect for the duration of the payments.
- You can access funds up to a predetermined amount, called a credit limit.
- Once you’ve paid off your revolving credit balance in full, you can use the money again, minus interest and other costs.
- You will pay interest on the balance transferred.
How Does Revolving Credit Work?
When a borrower is approved for a revolving loan, the bank or financial institution sets a credit limit that can be used in whole or in part repeatedly. A credit limit is the maximum amount that a financial institution can lend to a customer who wants money.
Revolving loans are usually approved without an expiration date. The bank will continue the contract as long as your account is in good standing. Over time, banks may increase credit limits to encourage their most loyal customers to spend more.
We are very experienced. “Understanding Revolving Credit.”
- Borrowers pay interest monthly on their current loan. Because of the convenience and flexibility of revolving loans, they typically charge higher interest rates than traditional installment loans. Revolving loans can have variable interest rates that can be adjusted. Revolving loan costs vary.
- A home equity line of credit (HELOC) can be obtained at a slightly higher interest rate than a mortgage. A HELOC is a second mortgage that uses the equity in your home as collateral. On the other hand, the average interest rates on credit cards are quite high. In April 2023, the average credit card interest rate exceeded 20%.
Revolving Credit Examples
Advantages and Disadvantages of Revolving Credit
The biggest advantage of a revolving loan is that it gives borrowers the flexibility to access funds when they need them. Many small, medium and large businesses rely on revolving credit to maintain constant access to cash through seasonal fluctuations in costs and sales.
dvantages:
- Flexibility in Spending: Discuss how revolving credit provides flexibility in making purchases and managing expenses.
- Convenient Access to Funds: Highlight the ease of accessing funds whenever needed without reapplying for a loan.
- Builds Credit History: Explain how responsible use of revolving credit can help build a positive credit history.
- Rewards and Perks: Discuss any rewards programs or perks associated with certain revolving credit accounts.
- Interest-Free Grace Period: Explain the benefit of an interest-free period if the balance is paid in full each month.
- Emergency Fund Access: Emphasize how revolving credit can serve as an emergency fund during unexpected expenses.
Disadvantages:
- High-Interest Rates: Discuss the typically higher interest rates associated with revolving credit compared to other forms of credit.
- Debt Accumulation: Highlight the risk of accumulating debt if balances are not paid in full, leading to interest charges.
- Minimum Payment Trap: Explain how making only minimum payments can prolong debt repayment and increase interest costs.
- Credit Score Impact: Discuss how high credit utilization can negatively impact credit scores.
- Potential for Overspending: Address the temptation to overspend with available credit, leading to financial strain.
- Fees and Penalties: Discuss any fees, such as annual fees or late payment penalties, associated with revolving credit accounts.
Revolving loans can be a risky form of lending if not managed wisely. An important part of your credit score (30%) is your credit utilization rate. High credit utilization can have a negative impact on your credit score. Most credit experts recommend keeping this ratio under 30%.
How Can Revolving Credit Help Your Credit Score?
A revolving loan is a line of credit that can be a valuable financial tool to help you pay off your loan. If you use revolving credit responsibly, you can build your credit score and enjoy rewards like cash back and travel points. If you have a revolving line of credit, your credit score can suffer if you don’t make the minimum payment on time.
- Payment History: Timely payments on your revolving credit accounts contribute significantly to your credit score. Consistently paying at least the minimum amount due on time reflects positively on your credit report.
- Credit Utilization Ratio: Revolving credit accounts, like credit cards, provide a credit limit that you can utilize. Maintaining a low credit utilization ratio (the amount of credit used compared to the total credit available) can boost your credit score. Experts often recommend keeping this ratio below 30% to positively impact your score.
- Credit Mix: Having a diverse mix of credit types, including revolving credit (such as credit cards) along with installment loans (like car loans or mortgages), can positively influence your credit score. It demonstrates your ability to manage different types of credit responsibly.
- Credit History Length: Keeping revolving credit accounts open for a long time can lengthen your credit history, which is a positive factor in credit scoring models. It showcases your credit management over an extended period, potentially boosting your score.
However, it’s crucial to use revolving credit wisely. Utilize only the credit you need, pay balances on time, and avoid carrying high balances to reap the benefits without adversely affecting your credit score.